MetaService Architecture
Overview
MetaService (also known as Placement Center) is the metadata management and cluster coordination center of RobustMQ. It serves as the brain of the entire system, responsible for managing cluster metadata, node coordination, fault detection, and recovery. Built on the Raft consensus algorithm, MetaService ensures high availability and strong consistency of cluster metadata.
Design Principles
MetaService is designed with the following core principles:
- High Availability: Raft-based consensus ensures cluster availability even with node failures
- Strong Consistency: All metadata operations are strongly consistent across the cluster
- Fault Tolerance: Automatic detection and recovery from node failures
- Scalability: Support for dynamic cluster membership changes
- Performance: Optimized for low-latency metadata operations
Architecture Overview
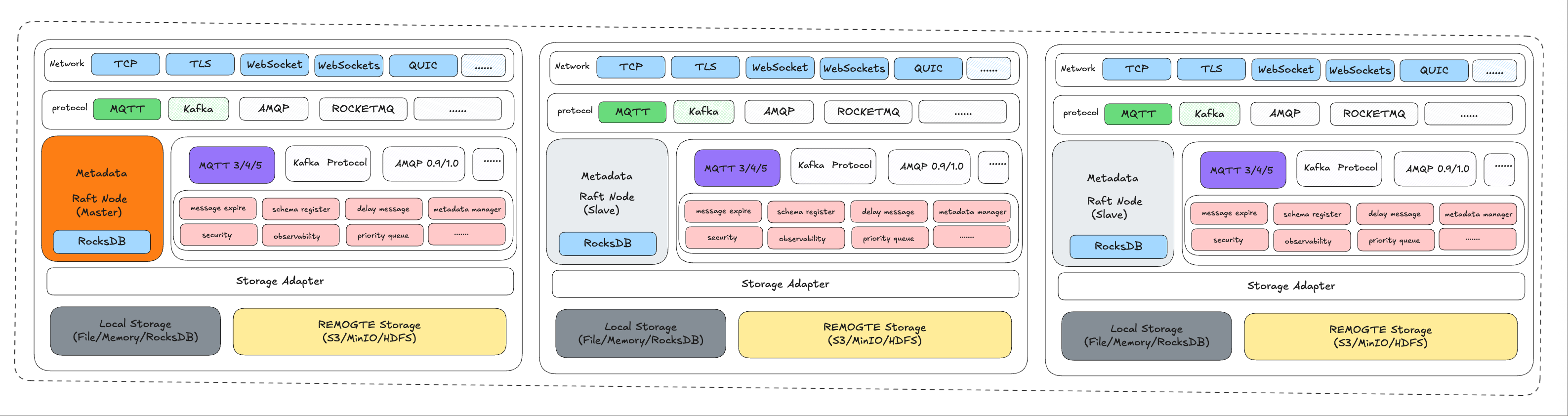
MetaService follows a layered architecture with clear separation of concerns:
1. Service Layer
- gRPC Services: External API interfaces for cluster operations
- Internal Services: Protocol-specific service implementations
- Service Discovery: Node registration and discovery mechanisms
2. Core Layer
- Cache Management: High-performance in-memory metadata cache
- Cluster Controller: Central coordination and control logic
- Heartbeat Management: Node health monitoring and failure detection
- Metrics Collection: Performance and operational metrics
3. Raft Layer
- Consensus Engine: Raft algorithm implementation for distributed consensus
- State Machine: Metadata state management and transitions
- Log Store: Persistent log storage for Raft operations
- Network Layer: Inter-node communication and message passing
4. Storage Layer
- RocksDB Engine: Persistent storage for metadata and logs
- Data Routing: Request routing to appropriate storage handlers
- Schema Management: Data schema and structure management
Core Components
Service Layer (src/server/)
The service layer provides external APIs and internal service implementations.
gRPC Services
- PlacementCenterService: Main gRPC service for cluster operations
- MQTT Service: MQTT-specific metadata operations
- Journal Service: Storage-related metadata operations
- KV Service: Key-value metadata operations
Service Implementations
pub struct GrpcPlacementService {
raft_machine_apply: Arc<StorageDriver>,
cluster_cache: Arc<CacheManager>,
rocksdb_engine_handler: Arc<RocksDBEngine>,
client_pool: Arc<ClientPool>,
journal_call_manager: Arc<JournalInnerCallManager>,
mqtt_call_manager: Arc<MQTTInnerCallManager>,
}Key Responsibilities:
- Handle external gRPC requests
- Route requests to appropriate internal services
- Manage client connections and authentication
- Provide service discovery and health checks
Core Layer (src/core/)
The core layer contains the essential business logic and coordination mechanisms.
Cache Manager (cache.rs)
- In-Memory Cache: High-performance metadata caching
- Cache Invalidation: Automatic cache consistency management
- Cache Warming: Proactive cache population for performance
- Memory Management: Efficient memory usage and garbage collection
Cluster Controller (controller.rs)
pub struct ClusterController {
cluster_cache: Arc<CacheManager>,
placement_center_storage: Arc<StorageDriver>,
stop_send: broadcast::Sender<bool>,
client_pool: Arc<ClientPool>,
journal_call_manager: Arc<JournalInnerCallManager>,
mqtt_call_manager: Arc<MQTTInnerCallManager>,
}Key Responsibilities:
- Cluster coordination and management
- Node lifecycle management
- Fault detection and recovery
- Load balancing and routing decisions
Heartbeat Management (heartbeat.rs)
- Node Health Monitoring: Continuous health checks of cluster nodes
- Failure Detection: Automatic detection of failed nodes
- Recovery Coordination: Orchestrate recovery procedures
- Health Metrics: Collect and report node health statistics
Raft Layer (src/raft/)
The Raft layer implements distributed consensus for metadata consistency.
Raft Node (raft_node.rs)
pub struct Node {
pub node_id: u64,
pub rpc_addr: String,
}
pub type NodeId = u64;Key Features:
- Leader Election: Automatic leader election and failover
- Log Replication: Consistent log replication across nodes
- Membership Changes: Dynamic cluster membership management
- Snapshot Management: Efficient snapshot creation and restoration
State Machine (store/state_machine_store.rs)
- State Transitions: Manage metadata state changes
- Log Application: Apply committed log entries to state
- Snapshot Creation: Create consistent snapshots of state
- Recovery: Restore state from snapshots and logs
Network Layer (network/)
- Inter-Node Communication: Efficient communication between Raft nodes
- Message Serialization: Optimized message serialization/deserialization
- Connection Management: Reliable connection handling
- Load Balancing: Distribute network load across nodes
Storage Layer (src/storage/)
The storage layer provides persistent storage for metadata and logs.
RocksDB Engine (rocksdb.rs)
- Persistent Storage: Durable storage for metadata and logs
- High Performance: Optimized for metadata access patterns
- Compaction: Automatic data compaction and optimization
- Backup/Restore: Data backup and recovery capabilities
Data Routing (raft/route/)
- Request Routing: Route requests to appropriate handlers
- Protocol Support: Support for different data types and protocols
- Batch Processing: Efficient batch processing of operations
- Error Handling: Comprehensive error handling and recovery
Data Flow Architecture
Metadata Operations Flow
- Client Request: Client sends metadata operation request
- Service Layer: gRPC service receives and validates request
- Cache Check: Check in-memory cache for data
- Raft Consensus: If cache miss, propose operation to Raft cluster
- Log Replication: Replicate operation across cluster nodes
- State Application: Apply operation to state machine
- Cache Update: Update in-memory cache with new data
- Response: Return result to client
Node Management Flow
- Node Registration: New node registers with cluster
- Health Monitoring: Continuous heartbeat monitoring
- Failure Detection: Detect node failures through missed heartbeats
- Recovery Coordination: Coordinate recovery procedures
- Load Rebalancing: Rebalance load after node changes
- Membership Update: Update cluster membership
Consensus Flow
- Leader Election: Elect leader through Raft consensus
- Log Proposals: Leader proposes operations to followers
- Vote Collection: Collect votes from majority of nodes
- Commit: Commit operations after majority agreement
- State Update: Update state machine with committed operations
- Response: Return results to clients
Protocol-Specific Controllers
MQTT Controller (controller/mqtt/)
- Session Management: Manage MQTT client sessions
- Topic Routing: Route messages to appropriate topics
- Subscription Management: Handle topic subscriptions
- QoS Coordination: Coordinate QoS levels across brokers
Journal Controller (controller/journal/)
- Storage Coordination: Coordinate with storage nodes
- Data Replication: Manage data replication across storage nodes
- Garbage Collection: Coordinate garbage collection operations
- Storage Health: Monitor storage node health
Performance Characteristics
Latency
- Cache Hits: Microsecond-level response times
- Cache Misses: Millisecond-level response times
- Consensus Operations: Sub-second consensus times
- Node Failures: Second-level failover times
Throughput
- Metadata Operations: High-throughput metadata operations
- Concurrent Requests: Support for high concurrent request loads
- Batch Operations: Efficient batch processing capabilities
- Network Efficiency: Optimized network utilization
Scalability
- Cluster Size: Support for clusters of varying sizes
- Dynamic Scaling: Dynamic addition/removal of nodes
- Load Distribution: Automatic load distribution across nodes
- Resource Utilization: Efficient resource utilization
Fault Tolerance and Recovery
Node Failure Handling
- Automatic Detection: Automatic detection of failed nodes
- Quorum Maintenance: Maintain quorum for consensus operations
- Data Replication: Ensure data replication across healthy nodes
- Service Continuity: Maintain service availability during failures
Recovery Procedures
- Node Recovery: Automatic recovery of failed nodes
- Data Synchronization: Synchronize recovered nodes with cluster
- State Restoration: Restore consistent state across cluster
- Service Restoration: Restore full service functionality
Split-Brain Prevention
- Majority Consensus: Require majority agreement for operations
- Leader Election: Single leader at any time
- Network Partition Handling: Handle network partitions gracefully
- Consistency Guarantees: Maintain strong consistency guarantees
Monitoring and Observability
Metrics Collection
- Performance Metrics: Latency, throughput, and error rates
- Cluster Metrics: Node health, cluster size, and membership
- Raft Metrics: Consensus performance and log replication
- Storage Metrics: Storage utilization and performance
Health Monitoring
- Node Health: Individual node health status
- Cluster Health: Overall cluster health assessment
- Service Health: Service availability and performance
- Resource Health: Resource utilization and availability
Logging and Tracing
- Structured Logging: Comprehensive structured logging
- Distributed Tracing: End-to-end request tracing
- Audit Logging: Security and compliance logging
- Debug Logging: Detailed debug information
Configuration and Deployment
Configuration Management
- Cluster Configuration: Cluster membership and settings
- Raft Configuration: Raft algorithm parameters
- Storage Configuration: Storage engine settings
- Network Configuration: Network and communication settings
Deployment Options
- Standalone: Single-node deployment for development
- Cluster: Multi-node cluster deployment
- Cloud: Cloud-native deployment with auto-scaling
- Hybrid: Mixed deployment across environments
Security Configuration
- Authentication: Node authentication mechanisms
- Authorization: Access control and permissions
- Encryption: Data encryption in transit and at rest
- Audit: Security audit and compliance features
Integration with Other Components
Broker Integration
- Service Discovery: Provide service discovery for brokers
- Load Balancing: Coordinate load balancing across brokers
- Health Monitoring: Monitor broker health and performance
- Configuration Management: Manage broker configurations
Storage Integration
- Storage Coordination: Coordinate with storage nodes
- Data Management: Manage data placement and replication
- Storage Health: Monitor storage node health
- Capacity Management: Manage storage capacity and utilization
Client Integration
- Service Discovery: Provide service discovery for clients
- Authentication: Handle client authentication
- Authorization: Manage client permissions and access
- Configuration: Provide configuration to clients
Future Enhancements
Planned Features
- Enhanced Monitoring: Advanced monitoring and alerting
- Performance Optimization: Further performance improvements
- Security Enhancements: Additional security features
- Cloud Integration: Enhanced cloud provider integration
Scalability Improvements
- Larger Clusters: Support for larger cluster sizes
- Geographic Distribution: Support for geographically distributed clusters
- Multi-Region: Multi-region deployment support
- Edge Computing: Edge computing deployment support
Conclusion
MetaService is the critical component that ensures the reliability, consistency, and performance of RobustMQ clusters. Its Raft-based consensus architecture provides strong consistency guarantees while maintaining high availability and fault tolerance. The layered design with clear separation of concerns makes it maintainable and extensible.
The combination of in-memory caching, efficient consensus algorithms, and robust storage mechanisms enables MetaService to handle high-throughput metadata operations while maintaining sub-second response times. This makes it suitable for demanding production environments requiring high availability and strong consistency.
This document provides a comprehensive overview of MetaService architecture. For more detailed information about specific components, please refer to the individual component documentation.
